
- Android sqlite database example how to#
- Android sqlite database example android#
- Android sqlite database example software#
- Android sqlite database example code#

The layered architecture is shown i the figure below. While the app is very simple the plumbing around constructing a database is complex at first. These various steps are shown in the screen dumps below of the app.
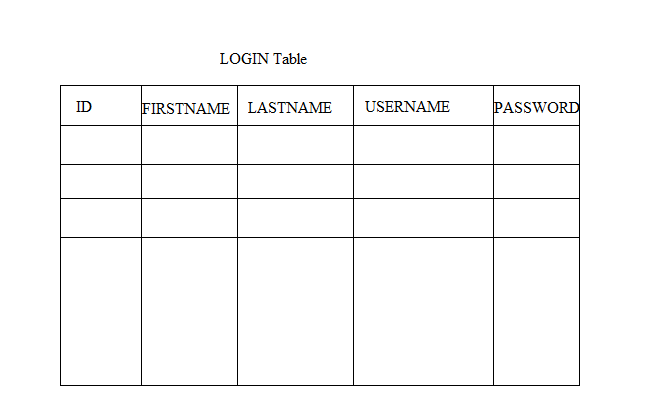
Finally, the user can delete all items in the data base. As the user adds and deletes items (i.e., comment) the UI reflects that. When the application first starts up there is not existing database so it displays no items. The application is very simple but allows us to understand how the database is set up and accessed. So comment is the main object that the user deals with. Comments can be added one at a time, deleted (from the top) one at a time or all comments can be deleted. The application simply allows the user to add canned comments to the database and display them to the UI. When an application creates a private database it is stored in the following folder on your phone - but you have to root your phone to see it: /data/data//database Database demo app SQLite is a transactional database engine which is lightweight: in overhead, fast performance, small footprint and implemented as a c library. More on content providers in the next lecture let's get back to databases. The database plumbing is of little interest to applications, they just want to get the data and manage it in the app domain. So the application talks content provider language and is unaware of how data is stored or the internals of the database - it abstracts the data source and provides management APIs to the data. Importantly, content providers provide a generic interface to a data source by decoupling the data storage layer (the app's database) from the application layer. If any application wanted to share SQLite its data (e.g., contact list) with other applications running in your phone it would use Content Providers - content providers provide a uniform way to store, share and consume structured between applications but also within a single application (yes you set up an SQLite database and wrap it in a content provider to manage data). The database access is restricted to the app that created it.
Android sqlite database example android#
Android sqlite database example code#
This demo code is taken from Lars Voglel's tutorial on SQLite and slightly modified to include the delate all option. Simple use of the camera databasedemo.zip.The demo code used in this lecture include: The SQLite layer: finally the SQLiteOpenHelper plumbing exposed!.The data storage layer: CommentsDataSource.Performance issues: CursorLoader and asynchronously to cursor data.We will also tie databases to Content Providers - another important tool in the Android toolbox. I love abstraction - it's a powerful idea and allows you to hide the unnecessary details from the app designer. Abstraction is heavily leverage in use of SQLite on mobiles such as Android.
Android sqlite database example software#
I have tried to describe the software architecture around three layers: the app layer, data storage layer, and the SQLite layer. If you've not used SQLite (an industry standard and great for mobiles) before then this should be cool. We will relate this simple example to the SQLite database you need to design and implement as part of MyRuns3.
Android sqlite database example how to#
In this lecture, we will discuss how to use Android SQLite database through a simple demo project example. Android supports the very simple and very cool SQLite. Structured or relational data such as your list of contacts is best stored and managed using relational databases. Unstructured data such as a jpeg file or html page is best stored in files.

There are many ways to handle data on mobile devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
